luogu#P9700. [GDCPC 2023] Peg Solitaire
[GDCPC 2023] Peg Solitaire
题目描述
is a single-player boardgame on a chessboard with rows and columns. Each cell of the chessboard either is empty, or contains a chesspiece. Initially, there are chesspieces on the chessboard.
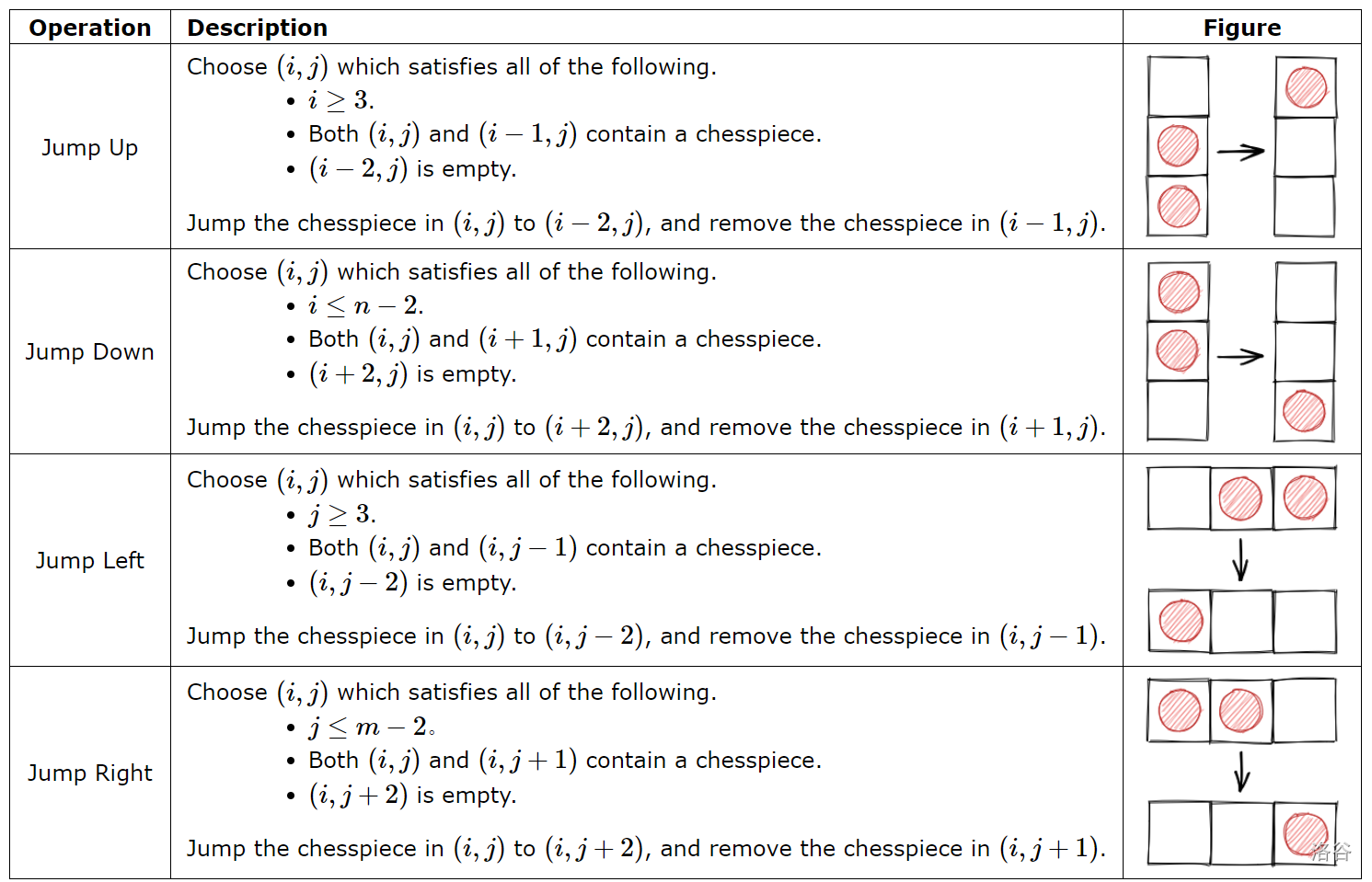
During the game, the player can choose a chesspiece, jump it over an adjacent chesspiece into an empty cell, and finally remove the chesspiece which is jumped over. More precisely, let be the cell on the -th row and the -th column, the player can perform operations of the following four types.
Given the initial state of the chessboard, the player can perform the operations any number of times (including zero times). Calculate the minimum possible number of chesspieces remaining on the chessboard.
输入格式
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer () indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains three integers , and (, ) indicating the number of rows and columns of the chessboard and the initial number of chesspieces.
For the following lines, the -th line contains two integers and (, ) indicating that there is a chesspiece in the cell on the -th row and the -th column at the beginning. Except from these cells, all other cells are empty at the beginning. The positions of these cells contain no duplicate.
输出格式
For each test case output one line containing one integer indicating the minimum possible number of chesspieces remaining on the chessboard.
题目大意
【题目描述】
独立钻石是一种单人桌游。游戏在 行 列的棋盘上进行,棋盘上的每一格要么是空格,要么有一枚棋子。一开始,棋盘上共有 枚棋子。
在游戏中,玩家可以选择一枚棋子,将它跳过相邻棋子到空格上,并移除被跳过的棋子。具体来说,令 表示位于第 行第 列的格子,玩家可以执行以下四种操作。

给定一个初始的棋盘,求经过任意次操作(包括零次)之后,棋盘上最少能剩余几枚棋子。
【输入格式】
有多组测试数据。第一行输入一个整数 ()表示测试数据组数。对于每组测试数据:
第一行输入三个整数 , 和 (,)表示棋盘的行数,列数和初始棋子的数量。
对于接下来 行,第 行输入两个整数 和 (,)表示一开始第 行第 列的格子里有一枚棋子。除了这 个格子之外,其它格子一开始都是空格。这 个格子的位置不会重复。
【输出格式】
每组数据输出一行一个整数,表示经过任意次操作(包括零次)之后,棋盘上最少能剩余几枚棋子。
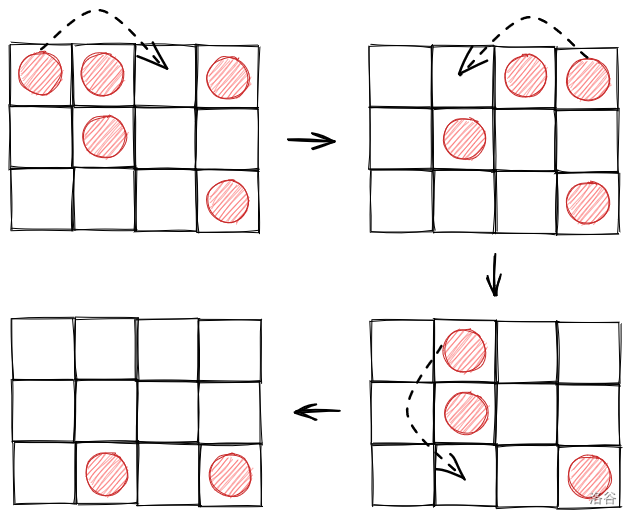
【样例解释】
第一组样例数据解释如下。
对于第二组样例数据,由于初始棋盘不存在空格,因此无法进行任何操作。
对于第三组样例数据,由于棋盘不足三格,因此无法进行任何操作。
3
3 4 5
2 2
1 2
1 4
3 4
1 1
1 3 3
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1 1
2 1
2
3
1
提示
The first sample test case is explained as follows.

For the second sample test case, as the chessboard does not contain empty cell at the beginning, the player cannot perform any operation.
For the third sample test case, as the chessboard has less than three cells, the player cannot perform any operation.
